
Regardless of how rapidly and efficiently a venture is finished, partners won’t be upbeat if the nature of the item or administration doesn’t live up to their desires.
All in one, by what means can a director track the nature of their task and ensure it meets the prerequisites of partners? So, the secret here is Quality Affirmation.
As we know, these days with digitalization, Apps are more towards cloud-based solutions to any specific problem-solving. So apps are mostly running in sandbox mode or in other different devices that are supported with tablets or wearables.
With this, testing is a necessary and on-going process for any mobile application.
What Is Quality Assurance?
Quality affirmation is an approach to maintain a strategic distance from botches in the task’s item or administration, and consequently forestall issues for your partners.
It’s the piece of value the executives that centers around keeping up the trustworthiness of the item or administration.
That gives partners the certainty that their quality prerequisites will be met. It is, in this way, a primary mainstay of a task the board.
Standards of Quality Assurance
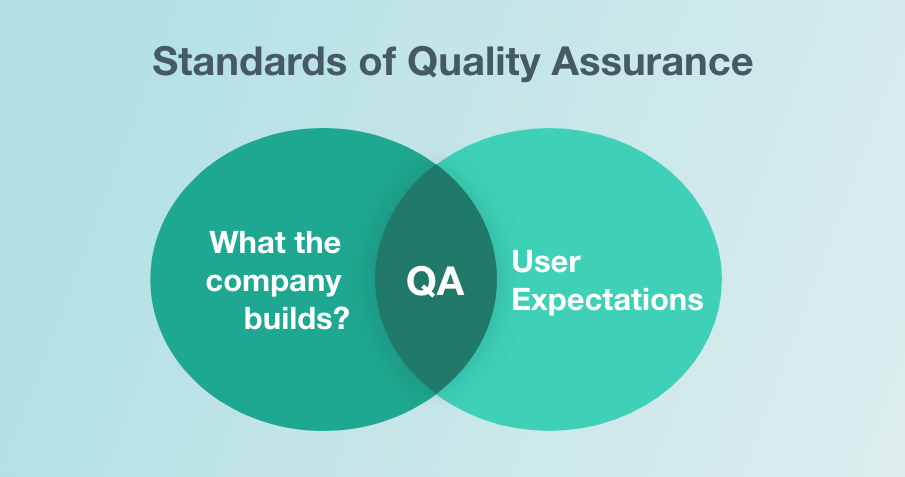
There are two standards to quality confirmation. One is “fit for a reason,” which means the item or administration meets its proposed reason. The other is “correct first time,” in which any mix-ups are quickly managed.
With the two above standards in play, the objective is to make the item or administration work accurately constantly through the administration of the factors in the task.
To do as such, quality confirmation includes the administration of the nature of crude materials, congregations, items, and segments.
Here are the 4 Common Mobile App Quality Issues
- Execution issues
As the client base of an application expands, the exhibition of an application is surely influenced. Execution issues represent almost 30% of objections on the Appstore and Play Store.
It is accurate to know about the quantity of simultaneous client limit that would begin influencing the exhibition of the application and at what time it can recover.
Moreover, designers frequently will, in general, overlook the heap an application puts on the gadget, it’s a battery, RAM, and information use. Continuously ensure the utilization is inside industry limits.
- Usefulness issues
Usefulness issues manage to distinguish the irregularities epidemic in the client excursion and route stream of an application.
The application should assist a utilitarian “User Interface” that meets the practical necessities and needs of users. Here, the critical zones to test includes:
- The development procedure of the application. Simply, join and login process
- Gadget capacities including the camera, sensors, screen direction and information techniques.
- Mistake notification, and the application redesign process.
- Convenience issues
Manages to decide that it is so natural to utilize the application interface. The interface capacities ought to be clear and not make any mistaken assumptions.
There shouldn’t be any glitches in getting to any usefulness offered by the application.
- Security issues
A handy yet uncertain application can prompt serious outcomes. The application ought to consistently be tried based on:
- Classification: Are legitimate encryption strategies used to make sure about private information?
- Validation: Is the application of confirming a client accurately before giving information?
- Approval: Is the application requesting access to just the necessary administrations on your gadget?
- Capacity: Is the information put away locally on the gadget appropriately encoded?
- Web Services: Is the application cooperating with web administrations utilizing secure conventions?
Affirmation, however, is progressively about the execution of assessment and organized testing all through each period of the task.
The thing that matters involves where the center happens in an undertaking. Quality control is increasingly worried about quality before in the task procedure.
Quality Assurance for Mobile Application Development
Underneath you can see a case of how Quality Assurance can be coordinated into the application improvement process.
- Coding – Engineer composes the code, QA pro composes robotized tests.
- Pull Request – Engineer enlightens others concerning another piece of the code.
- Execution of computerized Tests – Programmed tests which check whether new changes didn’t break any previously actualized functionalities.
- Static Code Analysis – Code analysis is where code is checked by an uncommon program, which confirms if the code satisfies the great guidelines set by our advancement group.
- Executing Unit Tests – Mechanized tests that approve if every unit of the product proceeds as structured.
- Executing UI Integration Tests – Automated tests that check if the application parts are accurately incorporated.
- Virtual Device Testing – Ir is used to discover crashes in Android applications. It recreates certain application use.
- Code Review – Each bit of code composed by one designer is affirmed at any rate by another engineer.
- Execution Testing – the most recent alpha/beta discharge is conveyed to the customer and analyzers.
- Manual Tests – A manual testing of the application dependent on determining use cases. QA pros made it.
The testing procedure is rehashed ordinarily during the development phase. Best practices for Quality Assurance:
- Make a robust testing environment by selecting discharge rules.
- Next, apply automated testing to high regions to set aside your cash. It assists in securing the whole procedure.
- Assign time appropriately for each procedure. As it is essential to organize bugs fixes dependent on programming usage.
- A structure devoted to security and execution of the testing group.
- Reproduce client accounts like a creation situation
Wrapping up
Quality Assurance is to check whether the services or product build is fit for use or not. For that, the app development company should have procedures and principles to be followed, which should be enhanced with an intermittent premise. It focuses on the most part on the nature of the product that is given to the clients during or after usage of the product.








